In the complex and intricate world of construction, the coordination between various engineering disciplines is crucial. Two of the most
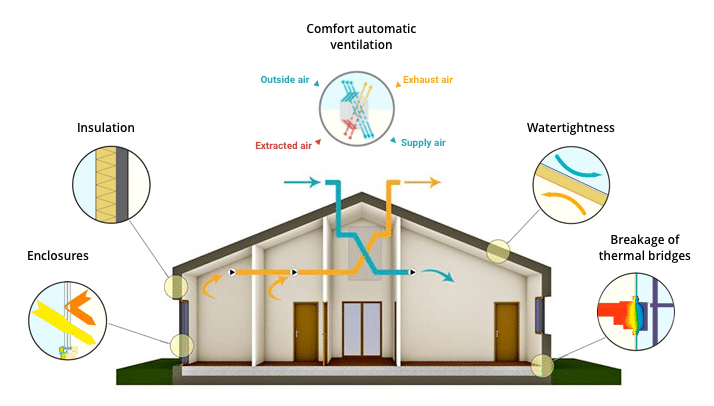
Passive Houses are gaining popularity worldwide as a sustainable and energy-efficient building design. The term “passive” means that the house does not rely on active heating or cooling systems to maintain a comfortable temperature. Instead, it relies on passive heating and cooling techniques that make use of natural resources to provide comfortable indoor temperatures. In this blog post, we will discuss what a Passive House is, its advantages, and MEP design tips and considerations to keep in mind while designing a Passive House.
A Passive House is a building design that focuses on energy efficiency and sustainable living. The concept of Passive Houses originated in Germany in the 1990s, but it has gained popularity worldwide in recent years. Passive Houses are designed to reduce energy consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional buildings. They use natural resources such as sunlight, air, and earth to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
There are several advantages of building a Passive House. Here are some of them:
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) design plays a crucial role in the design of a Passive House. Here are some MEP design tips and considerations to keep in mind while designing a Passive House:
In conclusion, MEP design plays a crucial role in the design of a Passive House. Passive Houses are designed to be energy-efficient, sustainable, and comfortable. Proper MEP design can help achieve these goals by ensuring that the building systems work together to create an efficient and comfortable indoor environment. By following the tips and considerations outlined in this blog post, you can design an effective MEP system for your Passive House.
About Author
InnoDez