Air filtration and industrial ventilation are important considerations when creating a ventilation design for a warehouse setting. In addition, these
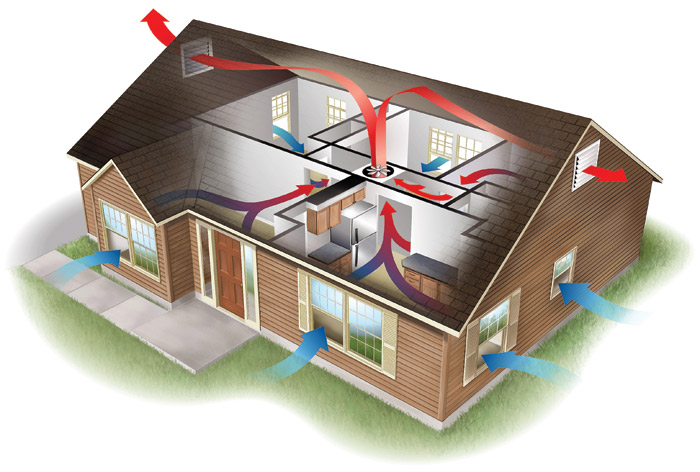
Introduction
IAQ (Indoor Air Quality) refers to the quality of air around and within buildings. It plays an important role in HVAC design. More importantly, it determines the comfort and health of the occupants. For this, it’s good to increase the rate at which outdoor comes into the building. It will help to control temperature, odors, humidity, and pollutants. All these factors can affect the comfort and health of the occupants. Statistics show that enhancing indoor ventilation will minimize the risk of virus transmission.
However, ventilation rates in buildings can be a complicated topic. Especially since different spaces have varying recommended ventilation rates. Don’t worry though! In this blog, we’ll cover ventilation rates for different facilities recommended by ASHRAE. This includes facilities like homes, schools, hospitals, residential and offices. Understanding this will help you determine the amount of ventilation a building needs.
ASHRAE stands for the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating & Air-Conditioning Engineers. In its Standard 62.1, ASHRAE suggests the ventilation rates for different buildings. These guidelines specify the amount of air that should come into a room per hour
ASHRAE 62.1 – ‘Ventilation & Acceptable Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in residential buildings. According to this guideline, homes require more than 0.35 air changes/ hour of outdoor air.
However, this guideline doesn’t provide a fixed for the number for shops, schools, and offices. Instead, ventilation rates vary depending on the room size and occupancy. These factors help to determine the exact ventilation requirements for a particular space.
Ventilation rate refers to the combined outdoor rate. ASHRAE 62.1 specifies these rates based on cfm (cubic feet/ minute) per sq. ft. of floor space and per person. These factors are related to occupancy in facilities like supermarkets, museums, and offices.
According to ASHRAE 62.1, there are 2 types of pollutant sources in an indoor surrounding. These are;
If the building has both sources, you’ll need ventilation to ensure adequate dilution. To achieve that, you’ve to add the rates required to deal with each source separately. To make that easy, ASHRAE provides a combined outdoor air rate.
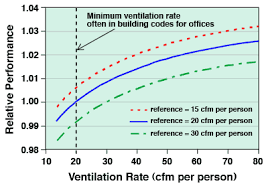
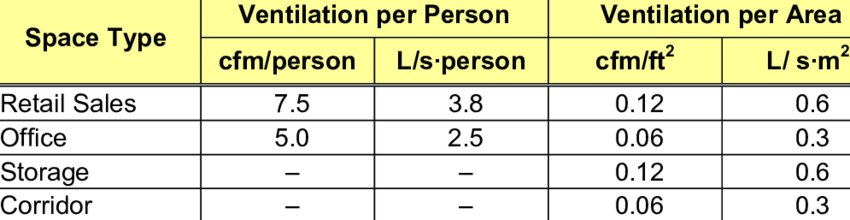
As we stated earlier, air change and ventilation rates can be calculated on a cfm/ person basis. If the number of building occupants increases, the ventilation rate will increase as well.
This rule is essential in facilities that experience changes in occupancy levels. For instance, the minimum combined outdoor air rate of galleries and museums is 9 cfm per person. Weight rooms in health clubs, however, require more than 26 cfm per person.
A Standard 62.1 analysis of the min. combined outdoor air rates show that occupancy type can impact ventilation requirements. So, occupancy type can also impact the room’s ventilation requirements in HVAC design. For instance, the seating area of an auditorium requires 5 cfm per person. On the contrary, offices require 17 cfm per person.
The ASHRAE Standard 62.1 is a practical guideline for ventilation rates in buildings. That could be offices, classrooms, homes, and offices. It provides the general ventilation rates that will maintain comfortable indoor environments.
However, the ventilation rates in this guideline may be too low in some situations. This means that the ASHRAE standard doesn’t apply in all situations. These circumstances include;
Conclusion
Bottom line, schools, homes, restaurants, and offices have different recommended ventilation rates. According to the standard ASHRAE 62.1, these rates can range from 0.35 to 8 air changes/ hour.
To learn more about ventilation rates for California buildings, contact InnoDez Design & Engineering. We’ll help to ensure that your existing and new building meets the minimum ventilation rates. This will help to mitigate adverse health effects and improve the IAQ for the occupants.
About Author
InnoDez