Design Tips for Converting Commercial Building to Residential Versatile reuse is the act of repurposing a structure with one use
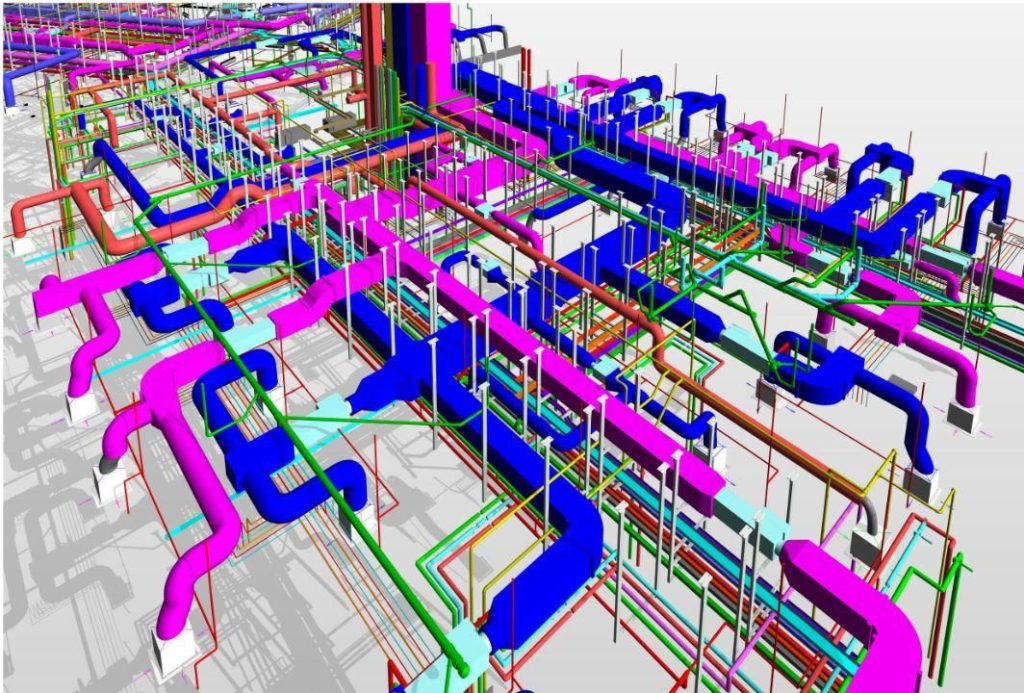
Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems are a type of HVAC system that can provide heating and cooling to multiple zones in a building using a single outdoor unit and multiple indoor units. VRF systems are becoming more popular in MEP design and engineering projects because of their energy efficiency, flexibility, and comfort. However, VRF systems also pose some challenges for MEP design and engineering professionals, such as installation, maintenance, and code compliance. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits and challenges of VRF systems for MEP design and HVAC design projects, and how InnoDez Design and Engineering Company can help you with your VRF system needs.
VRF systems are a type of HVAC system that use refrigerant as the medium to transfer heat between the outdoor unit and the indoor units. The outdoor unit consists of a compressor, a condenser, and an expansion valve, while the indoor units consist of fan coils, air handlers, or cassette units. The indoor units are connected to the outdoor unit by refrigerant piping, which can vary in length and diameter depending on the system configuration.
The key feature of VRF systems is that they can modulate the amount of refrigerant flowing to each indoor unit according to the heating or cooling demand of each zone. This allows VRF systems to provide simultaneous heating and cooling to different zones in a building, as well as to adjust the capacity of the system to match the load. VRF systems can also recover heat from one zone and transfer it to another zone, reducing the energy consumption of the system.
VRF systems offer several benefits for MEP design and HVAC design projects, such as: – Energy efficiency: VRF systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 40% compared to conventional HVAC systems, according to some studies. This is because VRF systems can adjust the capacity of the system to match the load, avoid overcooling or overheating, and recover heat from one zone and transfer it to another zone.
VRF systems can also use variable speed compressors, which can operate at lower speeds and consume less power than fixed speed compressors.
– Flexibility: VRF systems can provide heating and cooling to multiple zones in a building using a single outdoor unit and multiple indoor units. This reduces the space required for ductwork, mechanical rooms, and equipment. VRF systems can also accommodate different types of indoor units, such as wall-mounted, ceiling-mounted, floor-standing, or concealed units, which can suit different architectural styles and preferences. VRF systems can also be easily expanded or modified by adding or removing indoor units.
– Comfort: VRF systems can provide individual temperature control for each zone in a building, enhancing the comfort of the occupants. VRF systems can also provide better air quality by using filters, dehumidifiers, or fresh air intake in the indoor units. VRF systems can also operate quietly, as the outdoor unit is usually located away from the occupied areas and the indoor units use low-noise fans.
VRF systems also pose some challenges for MEP design and engineering projects, such as:
– Installation: VRF systems require careful planning and coordination during the installation phase, as they involve complex refrigerant piping networks that need to comply with safety codes and standards. The refrigerant piping also needs to be properly insulated, supported, sealed, tested, and labeled. The installation of VRF systems also requires skilled technicians who are trained and certified in handling refrigerant.
– Maintenance: VRF systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The maintenance of VRF systems includes checking the refrigerant levels and pressures, cleaning the filters and coils, inspecting the electrical components and connections, and performing diagnostic tests. The maintenance of VRF systems also requires specialized tools and equipment that can measure the refrigerant flow and temperature.
– Code compliance: VRF systems need to comply with various codes and standards that regulate the use of refrigerant in HVAC systems. These codes and standards include ASHRAE Standard 15 (Safety Standard for Refrigeration Systems), ASHRAE Standard 34 (Designation and Safety Classification of Refrigerants), International Mechanical Code (IMC), International Fire Code (IFC), National Electrical Code (NEC), among others. These codes and standards specify the maximum allowable refrigerant charge, refrigerant leak detection requirements, ventilation requirements, fire protection requirements, electrical requirements, among others.
InnoDez Design and Engineering Company is a professional MEP design and engineering company that provides MEP design and engineering services for various types of projects, including VRF system projects. We have the expertise, experience, and resources to help you with your VRF system needs, from design to installation to maintenance.
We can help you with:
– Design: We can design your VRF system according to your project specifications, budget, and goals. We can select the best VRF system configuration, equipment, and components for your project. We can also perform load calculations, energy modeling, and system optimization to ensure the energy efficiency and performance of your VRF system. We can also prepare the necessary drawings, documents, and permits for your VRF system project.
If you are looking for a professional MEP design and engineering company that can help you with your VRF system needs, contact us today at InnoDez Design and Engineering Company. We are ready to assist you with your VRF system project.
About Author
InnoDez